
Immune Enhancement and Memory Recovery
It was the sixth day lying on my couch feeling sick. This
Supporting you in Creating a Lifetime of Wellness, Vitality and Longevity
 Neurofeedback is a type of biofeedback that addresses cognitive imbalances revealed in a QEEG. This direct brain function training uses electrodes placed on specific areas of the scalp to record and amplify the QEEG, or brainwaves, and control auditory and visual feedback, which allows retraining of the brain to take place.
Neurofeedback is a type of biofeedback that addresses cognitive imbalances revealed in a QEEG. This direct brain function training uses electrodes placed on specific areas of the scalp to record and amplify the QEEG, or brainwaves, and control auditory and visual feedback, which allows retraining of the brain to take place.
We also incorporate LENS, or Low Energy Neurofeedback System, which was created as an alternative to medication for brain-based problems. Using a low power electromagnetic field, similar to the ones that surround digital watches, LENS is able to simultaneously monitor brain activity and carry feedback to specific sites on the brain.

It was the sixth day lying on my couch feeling sick. This

Prior to my traditional neurofeedback and LENS treatment, I was not particularly

Our 9-year-old son began experiencing severe anxiety when he was in 1st
 Neurofeedback is direct brain function training designed to address any imbalances revealed in your QEEG. It is also a type of biofeedback and is therefore also called EEG Biofeedback. It uses the electrodes (which act like tiny microphones) placed on specific areas of the scalp to record and amplify the EEG, or brainwaves, and control auditory, visual, and/or tactile feedback which allows learning to take place. This operant learning initiates self-regulation and enhances relaxation, both necessary components of good brain function.
Neurofeedback is direct brain function training designed to address any imbalances revealed in your QEEG. It is also a type of biofeedback and is therefore also called EEG Biofeedback. It uses the electrodes (which act like tiny microphones) placed on specific areas of the scalp to record and amplify the EEG, or brainwaves, and control auditory, visual, and/or tactile feedback which allows learning to take place. This operant learning initiates self-regulation and enhances relaxation, both necessary components of good brain function.
In another way, neurofeedback targets the underlying dysregulation in brain activity that can exacerbate and often cause clinical symptoms. This influence may also encourage neurological resilience with the induction of brain flexibility, relaxation, and a steadier central nervous system. For example, if one’s state of neuroanatomy and physiological health is over-stimulated or under-aroused, mental illnesses, with various symptoms may manifest behaviorally, psychologically, emotionally, and/or physically. Such disorders as anxiety and depression may have a base in neurophysiology, which consequently can be targeted for training. A brain with greater flexibility has the capacity to more healthily adapt to challenging life situations.

During a session, patients usually report feeling relaxed. They sit in a recliner and listen to sounds and/or play a video game on a computer screen using their brain to direct the action. When the desired brain wave state is achieved, the game progresses. It’s easy and fun. Remember, nothing is being put into your brain. We are simply “listening” to your brain wave activity through sensors, much like a doctor listening to your heart with a stethoscope, and feeding the information back to you. For this reason, it is known as “Neurofeedback.”
Created as an alternative to medication for brain-based problems, The LENS, or Low Energy Neurofeedback System, is an EEG biofeedback system used for the management of numerous difficulties and disorders. Using a low power electromagnetic field, similar to the ones that surround digital watches, LENS is able to simultaneously monitor brain activity and carry feedback to specific sites on the brain. Although the feedback signal is very weak, it produces a measurable change in the brainwaves.
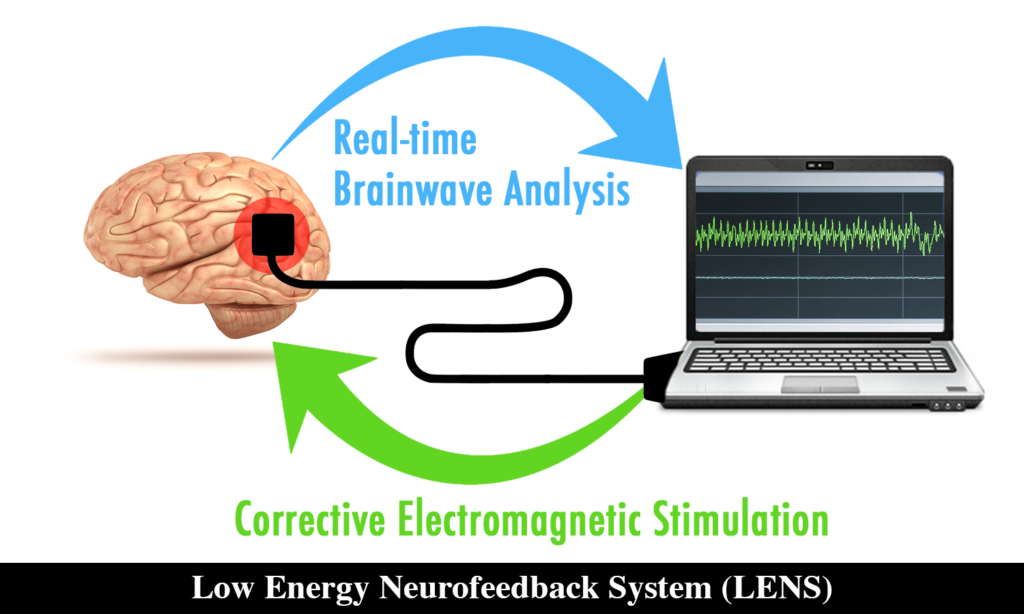
Traditional neurofeedback methods typically display information on a screen to guide the patient to develop healthier brainwave patterns and activity. The LENS system works on disrupting brain wave frequencies, or clusters of frequencies, that have been locked together into rigid patterns, and assist in developing more flexibility to pursue the tasks at hand.
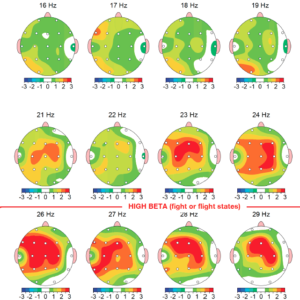
All LENS neurofeedback sessions begin with comprehensive mapping of the activity, or electrical amplitudes, of the brain at 21 different points. These readings provides the “map” of the amplitude of electrical activity in each part of the brain, which determines the order of sites in which to provide stimulation in subsequent sessions. Those sites with lower amplitudes are considered to be better functioning than those displaying higher amplitudes. Using a “whole-of-brain” approach, treatment is applied to all sites but proceeds from the sites with the lowest amplitude to the highest amplitude. This is so that the better functioning sites can respond and are recruited into the process of assisting the lower functioning sites later on in the treatment.
As far as what a LENS session involves, this is highly dependent on the person. For some people, one site with “ultra low feedback” is a completely sufficient treatment, whereas another person may respond best to 7 feedback sites in one session. In LENS there is one main axiom; “Less is more”. The duration of the “ultra low feedback” of the LENS is about 1/100th of a second out of typically 4 to 33 total seconds of exposure time.
The change can sometimes be noticed in a moment or may take a few hours to appear. This is often reported as a welcome feeling of calm and control, again our goal of relaxation. The brain recognizes efficiency and adopts it as a new way of working. Symptom improvement follows naturally. This is often noticed as a surprising increase in competence, functionality and relaxation.
LENS therapy may produce rapid improvement in a wide variety of issues. We typically see improved cognitive functions, motivation, mood, and motor skills. LENS often improves the quality of sleep. LENS users have benefited from reduced anxiety, seizures, migraines, post stroke effects, ADD/ADHD and even pain. Beyond these, LENS may help the best and brightest to be better and brighter in all realms of life.